| Field | Details |
|---|---|
| Invention Name | Automatic Temple Doors (Temple Mechanisms) |
| Short Description | Heat-triggered door-opening system using pneumatics and hydraulics |
| Approx. Date / Period | 1st century CE (Debated) Certainty: TartışmalıDetails |
| Geography | Alexandria (Roman Egypt) |
| Inventor / Source Culture | Heron (Hero) of Alexandria (Attributed in surviving tradition) |
| Category | Automation • Mechanical Engineering • Pneumatics |
| Importance |
|
| Need / Reason | Ceremonial timing and hands-free opening during temple routines |
| How It Works | Heat → pressure shift → water transfer → bucket weight → pulleys open doorsDetails |
| Core Materials / Tech | Sealed vessel • pipes • water • rope • pulleys • counterweight |
| First Use Context | Temple setting (ritual theatre and demonstration of ingenious mechanics) |
| Transmission / Spread | Manuscript copying and technical study across later centuriesDetails |
| Derived Developments | Pneumatic devices • automata • technical teaching traditions |
| Impact Areas | Engineering • architecture • education • public demonstration |
| Debates / Different Views | Dating and how directly the eclipse evidence fixes Heron’s lifespanDetails |
| Precursors + Successors | Precursors: pulleys, siphons, water management • Successors: richer mechanical automata, later pneumatic controls |
| Variations Influenced | Heat-triggered opening • different door linkages • tuned timing via vessel size and flow |
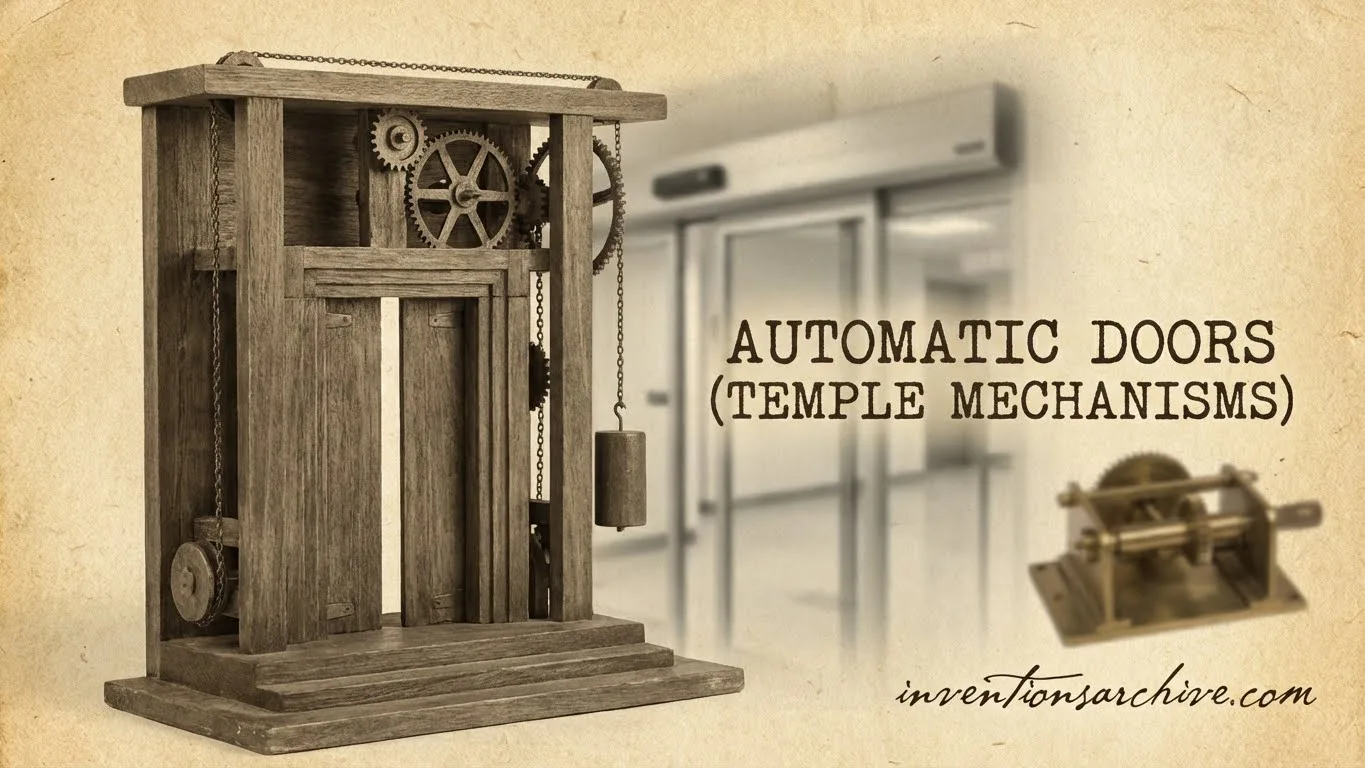
Automatic temple doors are one of the clearest ancient examples of automation built from simple forces: heat, air pressure, water, and gravity. The idea is elegant. A fire at an altar becomes a trigger, and a hidden mechanism turns that trigger into a smooth, deliberate opening of the doors.
Table of Contents
What It Is
These doors belong to the world of ancient automata: mechanisms that perform a visible action without a human hand on the moving part. The “automatic” element is not a sensor or a hidden operator. It is a chain of physical causes that begins with heat and ends in motion.
- Trigger: fire (heat at the altar)
- Converter: sealed air space becoming pressure
- Carrier: water moved by pressure change
- Actuator: bucket + weights pulling pulleys
Useful distinction: this is temple automation, not modern automatic doors. No electricity, no sensors, no motors. The power source is heat and the “logic” is built into weights and fluid flow.
Historical Setting
The most famous descriptions are tied to Heron of Alexandria, a figure associated with technical teaching and applied mechanics. His name is closely linked with Pneumatica, a tradition of devices driven by air, water, and sometimes heat. A key reason the temple doors endure in modern memory is simple: the action is immediately visible and the cause is deliberately indirect.
Why Temples
Temples offered a controlled stage where timing mattered. A door that opens after a ritual fire has meaning. It also showcases engineering skill without exposing its inner parts.
What People Saw
A calm sequence: fire, a pause, then doors swing open. The mechanism turns delayed cause into a strong effect.
Evidence and Dating
Heron’s lifespan is often placed around the 1st century CE, with arguments that connect his work to an eclipse dated to March 13, 62 CEDetails. At the same time, specialists continue to debate how tightly that eclipse reference fixes a biography, and whether it functions as strict evidence or as a worked exampleDetails. That is why “Debated” is the honest label for many timelines attached to these mechanisms.
Manuscript Survival
Whatever the exact date, the tradition is anchored by surviving copies of Pneumatica in later manuscript culture, including catalogued volumes with space for diagrams and technical drawingsDetails.
How It Worked
The classic explanation is a hidden conversion chain. A fire warms air in a sealed space. That pressure change shifts water between containers. The changing weight then pulls on a rope-and-pulley linkage tied to the door pivots. A well-known institutional summary notes the key idea: the heat produced by a burning offering is used to open the doorsDetails.
| Stage | Physical Change | Visible Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1) Heat | Air warms in a sealed space | Nothing yet (timed delay) |
| 2) Pressure | Pressure rises and pushes on water | Weight begins to shift |
| 3) Transfer | Water moves into a hanging container | Bucket descends |
| 4) Motion | Gravity acts through ropes and pulleys | Doors open |
| 5) Return | Cooling reduces pressure; balance resets | Doors close (by counterweight) |
Key Parts
- Heat zone: the altar area that warms a sealed volume
- Sealed vessel: where air expansion becomes pressure
- Water path: channels that allow transfer between containers
- Hanging load: a bucket that gains or loses weight
- Linkage: rope, pulleys, and counterweights that move the doors
In practical reconstructions, the beauty is not in exotic materials. It is in balance. The system must be near equilibrium so a modest change in water mass can tip it into motion, then let a counterweight return everything to rest.
Design Variations
“Automatic doors” is a family idea, not a single blueprint. Even within the same tradition, small choices change how the effect feels: faster, slower, smoother, heavier, quieter. The common thread is the same engine—heat producing pressure, pressure shifting water, and water shifting weight.
Door Layout
- Single-leaf doors (one pivot)
- Double-leaf doors (mirrored pivots)
- Different hinge geometry changes leverage
Timing Control
- Larger vessel: slower pressure change
- Narrower tube: gentler flow
- Heavier counterweight: firmer closing
Related Temple Devices
Temple doors sit beside other showpiece mechanisms often discussed in the same mechanical tradition: devices that dispense small amounts of liquid, instruments powered by water flow, and demonstrations that teach how air pressure behaves. The shared purpose is visibility—making an invisible cause feel real.
Why It Mattered
The lasting value of automatic temple doors is not that they predict today’s sliding entrances. Their value is that they show a mature grasp of systems thinking: a trigger, a converter, a transmission, a reset. That structure appears again and again in later engineering, even when the power source changes from heat to electricity.
- Energy literacy: turning heat into motion without a motor
- Control by balance: using counterweights for stable return
- Design clarity: separating cause from effect with a timed delay
- Teaching power: a compact lesson in pressure, flow, and mechanical advantage
Frequently Asked Questions
Were These Doors Truly “Automatic” By Modern Standards?
They were automatic in action but not modern in sensing. There is no electronic detection. The trigger is heat, and the response is created by pressure, water movement, and a weighted linkage.
Did The Fire Open The Doors Immediately?
Many reconstructions emphasize a short delay. Warming a sealed space and shifting water takes time, and that delay can be part of the intended effect. The moment still feels direct: fire first, then motion.
Why Is The Date Often Marked As Debated?
One line of argument connects Heron’s activity to an eclipse dated to 62 CE, while other scholarly work questions how firmly that kind of reference fixes a life spanDetails. That is why careful writing keeps a debated label on exact timelines.
What Makes This Mechanism So Influential In Invention History?
It is a clean demonstration of conversion and control. A small, hidden change produces a large, visible motion, then the system returns to rest through balance. That pattern—trigger, converter, actuator, reset—remains central to how engineers describe machines.